Knee instability is a common concern that significantly affects daily activities and the overall quality of life. This condition can arise from various factors, deeply impacting an individual’s mobility and strength. Jacksonville Physical therapy emerges as a crucial component of the rehabilitation process, employing tailored rehabilitation exercises aimed at enhancing knee strength and improving joint mobility.
Through professional guidance, these therapeutic interventions not only assist in recovery from injuries or surgeries but also empower individuals to proactively prevent future knee issues. In this article, we will delve into the complexities of knee instability, outlining its causes, symptoms, available treatment options, and effective strategies to restore mobility and confidence safely.
🤖 AI Summary: This article explores how physical therapy helps treat knee instability by addressing underlying causes such as ligament injuries, arthritis, and muscle imbalances. It outlines symptoms to watch for, rehabilitation techniques like strengthening exercises and bracing, and guidance on when to seek medical advice. With tailored treatment, patients can restore mobility, reduce pain, and prevent future injuries.
Key Takeaways
- Knee instability can impact daily activities significantly.
- Physical therapy is essential for rehabilitation and strengthening.
- Tailored rehabilitation exercises improve knee strength and joint mobility.
- Professional guidance aids in preventing future knee issues.
- Understanding causes and symptoms helps in managing knee instability effectively.
What is Knee Instability?
Knee instability describes a condition where the knee joint feels loose or incapable of supporting weight effectively. This issue often arises from various instability causes, such as injuries, degeneration of joint structures, or a combination of these factors. Individuals may experience a sensation of the knee giving out during activities, significantly increasing the risk of falls and further injuries.
Understanding the definition of knee instability is essential for proper management. The sensation can result from several underlying problems, including ligament tears, cartilage damage, or muscle weakness. Addressing these issues is crucial for maintaining the importance of knee health and ensuring overall mobility and safety.
Causes of Knee Instability
Knee instability can arise from various factors, contributing to discomfort and impaired movement. Understanding these causes is essential for effective management and rehabilitation. The following discusses some common contributors to knee instability.
Ligament Injuries
Ligament injuries, particularly to the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) and Posterior Cruciate Ligament (PCL), frequently lead to knee instability. These ligaments are crucial for maintaining knee stability during activities. Injuries may occur from high-impact sports or sudden twisting motions, causing pain and structural integrity loss. Recognizing the signs of ligament injuries is vital for prompt intervention.
Patellar Instability
Patellar instability involves the kneecap (patella) slipping out of its normal position, which can result from trauma or anatomical variations. Conditions such as dislocation, recurrent dislocations, or subluxations contribute to knee cap problems, affecting overall knee function. This instability often leads to discomfort and an unstable sensation during movement.
Arthritis
Arthritis, including degenerative joint disease and knee osteoarthritis, significantly impacts knee stability. This condition causes cartilage degeneration and joint inflammation, leading to symptoms like swelling and pain. As the knee joint becomes less stable, engaging in physical activities can become increasingly challenging and painful.
Muscle Imbalance or Weakness
Muscle imbalances can severely affect knee stability. Weakness in specific muscle groups, such as the quadriceps or hamstrings, can result in inadequate support for the knee. This lack of strength often increases susceptibility to instability and injury. Implementing targeted rehabilitation exercises plays a crucial role in enhancing knee strength and improving overall stability.
Symptoms of Knee Instability
The symptoms of knee instability can vary significantly among individuals. Common physical indications include a sensation of the knee giving way during activities. This may occur when walking or engaging in sports, leading to concern and hesitation.
Knee pain can accompany other symptoms such as:
- Swelling around the joint.
- Discomfort during movement.
- Difficulties with daily activities.
Individuals may notice that certain movements trigger discomfort. For instance, running or climbing stairs can exacerbate knee pain. The severity of these symptoms often correlates with the underlying causes of knee instability, making it essential to recognize these signs early. Seeking timely medical intervention can improve treatment outcomes and overall mobility.
Treatment Options
Addressing knee instability involves a range of treatment options tailored to meet individual needs. From conservative approaches like physical therapy to more invasive surgical interventions, these strategies aim to restore stability and reduce discomfort.
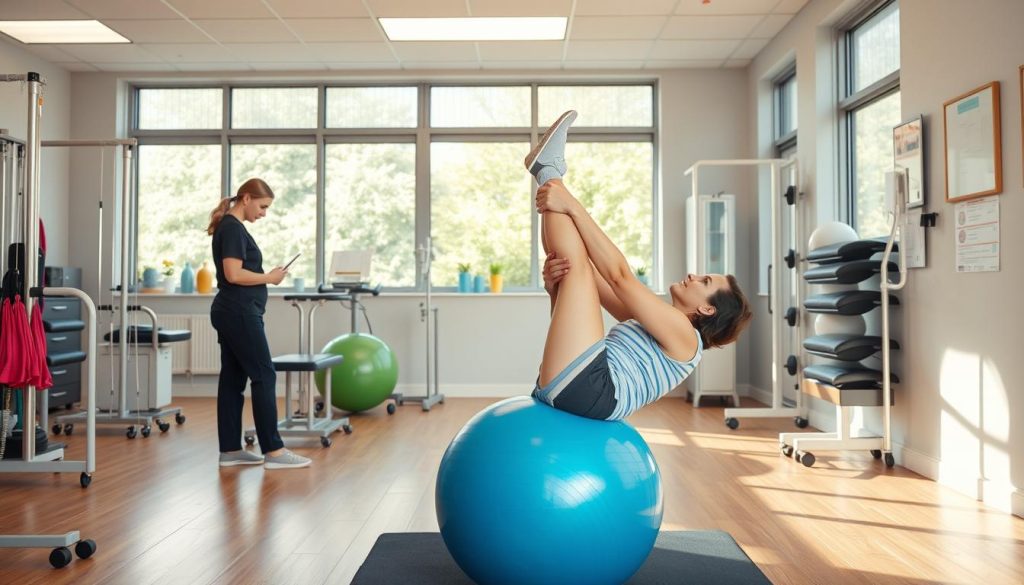
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy for knee instability serves as a cornerstone in recovery. This approach includes a personalized rehabilitation program designed to strengthen muscles surrounding the knee and improve flexibility. Key knee exercises such as squats, lunges, and lateral walks play a pivotal role. Patients typically experience notable improvements in knee strength and function over a consistent 4 to 6 week period.
Bracing
Knee bracing offers additional support during physical activities. A well-fitted brace acts as a stability aid, helping align the knee joint properly. This support not only reduces pressure on injured ligaments but also aids in a safer return to daily movements, enhancing overall knee support.
Medications
For many grappling with knee discomfort, anti-inflammatory medications can provide essential pain management. Over-the-counter NSAIDs (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs) give much-needed relief from pain and inflammation. Although these medications alleviate symptoms, they do not rectify the underlying instability.
Surgery
When conservative treatment options fail to deliver satisfactory results, surgical options may become necessary. Procedures like ACL reconstruction or arthroscopic surgery aim to repair structural problems within the knee. These surgical approaches can restore stability and improve overall function, allowing individuals to regain their active lifestyles.

When to Seek Medical Advice
Individuals experiencing knee pain should be vigilant about certain symptoms that may indicate the need for medical intervention. Key signs to see a doctor include:
- Persistent pain that doesn’t improve with rest.
- Significant swelling around the knee joint.
- A feeling of instability during movement.
- Inability to bear weight on the affected leg.
- Persistent stiffness or limited range of motion.
Seeking medical advice for knee pain can lead to a professional assessment that identifies underlying issues. If symptoms disrupt daily activities or progressively worsen, timely intervention is vital. Addressing knee problems early can prevent further damage and support a more effective recovery process.
Final Thoughts
- Seeking help early reduces long-term complications.
- Knee instability can be managed with the right therapy and expert care.
- Physical therapy focuses on strengthening, flexibility, and stability.
- Customized recovery plans lead to faster, more effective healing.
At Motion RX, we specialize in personalized rehabilitation solutions designed to treat knee instability at its root. Our team of experts will work with you to create a customized treatment plan that aligns with your goals and lifestyle—whether you’re recovering from an injury or managing chronic knee issues.
Don’t let knee instability hold you back—book a consultation with Motion RX Health today and take the first step toward lasting recovery and improved performance.
FAQ
What are the common causes of knee instability?
Common causes of knee instability include ligament injuries (especially to the ACL and PCL), patellar instability, osteoarthritis, and muscle imbalances that affect knee support. Understanding these underlying factors is essential for effective management.
What symptoms indicate knee instability?
Symptoms of knee instability can include a sensation of the knee giving way, pain during movement, swelling around the joint, and difficulties with daily activities, such as walking or standing. Recognizing these signs is important for timely intervention.
How can physical therapy help treat knee instability?
Physical therapy is crucial for addressing knee instability, focusing on strengthening surrounding muscles and enhancing flexibility. Tailored exercises like squats, lunges, and lateral walks can significantly improve knee function and stability over time.
Is bracing effective for knee instability?
Yes, bracing can provide additional support and stability to the knee, particularly during physical activities. It helps align the knee joint and reduces pressure on injured ligaments, promoting a safer return to mobility.
When should someone seek medical advice for knee instability?
Individuals should seek medical advice if they experience persistent knee pain, noticeable swelling, or a consistent feeling of instability that hinders daily activities. Early intervention can prevent further damage and guide effective treatments.
What other treatment options are available for knee instability?
Besides physical therapy and bracing, treatment options for knee instability can include over-the-counter or prescribed medications for pain relief, and in some cases, surgical interventions such as ACL reconstruction or arthroscopic surgery to address structural issues.



